Inflammation is a natural function of our body. When we get injured or fall ill, the lymphatic system of our body starts an immune reaction. It accelerates the productions of white blood cells and other immune substances allowing our body to repair the damaged area and protect itself from illness, infection, bacteria, and viruses.
So, inflammation is actually a good thing. Unfortunately, this is only a part of the whole story.
For some reason, the inflammatory process takes place unnecessarily and in areas of our body where it is not required. Then inflammation becomes a problem.
Let’s take a look at what is inflammation and how it affects the body plus nine strategies for lowering chronic inflammation.
Acute Vs Chronic Inflammation
There are two main types of inflammation.
Acute Inflammation:
It is the redness, warmth, swelling that develops after an injury or infection. Acute inflammation is a localized, short-term, rapid immune response of our body. Acute inflammation begins quickly and usually goes away in a matter of days.
Chronic Inflammation:
In contrast, chronic inflammation is a slowly developed, persistent, whole-body immune response. Due to constant exposure to some unwanted things, our body thinks, it is always under attack, so it keeps creating low-level inflammation continuously.
In the beginning, we don’t notice any symptoms, but slowly this low-grade inflammation develops diseases. So, we must control inflammation to live a healthy life.
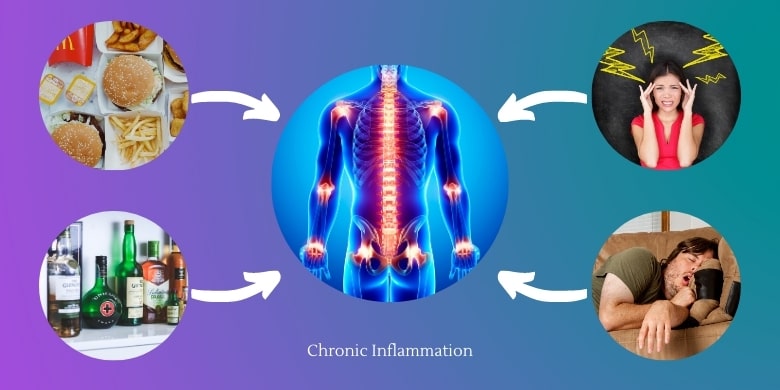
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Sugar: Processed sugar is a highly inflammatory substance. It has several negative effects on your body.
Food allergies: When you eat something you’re allergic to, your body becomes inflamed.
Nightshades: Most nightshade family vegetables including eggplants, tomatoes, and peppers trigger inflammation in many people.
Refined carbs: Regular food items like bread, pasta, cereals, biscuits contain refined wheat flour. They all are high glycemic foods that lack essential nutrients. These fibreless foods stick to our intestine walls and trigger inflammation.
Bad fats: Trans fats, hydrogenated oils, most refined oils – our body doesn’t like them very much.
High omega 6 fats: Sunflower oil, soy oil, peanut, and most vegetable oils contain a high level of omega 6 fats. Our body needs omega 6 fatty acids, but excess consumption of these fats can disbalance it.
Processed Foods: Processed meats such as hot dogs, sausages, etc., and all ready-to-eat packaged foods and snacks contain chemicals and preservatives that are not good for us and can certainly trigger inflammation.
Gluten: Gluten is a protein found in grains such as wheat, rye, and barley. People with gluten intolerance should avoid these grains.
Casein: Casein is a protein found in most dairy products. It can trigger inflammatory issues for some people.
Raw nuts and seeds: If you eat too many raw nuts, particularly if they are not germinated, then your body can become irritated as most raw nuts and seeds have enzyme inhibitors.
Alcohol: Alcohol weakens liver function. Without a properly functioning liver, our body cannot detoxify itself easily.
Stress: Chronic stress changes the behavior of our immune cells.
Signs of Chronic Inflammation
So, how do I know if I have inflammation?
Many people with chronic inflammatory disorders experience multiple symptoms. These symptoms can appear in a variety of ways all around the body.
The top 10 signs and symptoms of chronic inflammation include:
Fatigue
Excessive mucus production
Fever
Chills
Loss of energy
Loss of appetite
Body ache
Joint pain
Poor digestion
Skin issues
If you experience these symptoms regularly, you might have chronic inflammation.
The majority of people are more concerned with the pain and stiffness that comes with chronic inflammation. But, there are bigger problems other than that. Prolonged exposure to elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines leads to many diseases.
Inflammatory diseases cover a broad range of illnesses and disorders. Nearly all modern diseases are caused by chronic inflammation.
How to Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a major issue that affects people’s lives on a regular basis. Fortunately, there is something we can do to keep inflammation in check.
Here are nine strategies for lowering chronic inflammation:
Eliminate foods that cause inflammation: Try to limit all inflammatory foods. High Inflammatory foods include sugar, refined carbs, trans fats, deep-fried foods, processed foods, red meat, etc.
Eliminate food sensitives: Removing common allergic foods may help reduce inflammation. Foods like gluten, dairy, eggs, peanut, and nightshades like eggplant, tomato, pepper can trigger inflammation for some people. Keeping them out of your diet for a while may help.
Anti-inflammatory foods: Eating foods with anti-inflammatory properties can help you heal your inflammation. Start by consuming fresh fruits and vegetables that are in season. Eat foods that are rich in antioxidants, glutathione, resveratrol, nitric oxide, omega 3 fatty acids, and fiber, as well as foods that are nutrient-dense in general:
Leafy greens: Kale, Beet greens, Celery
Vegetables: Broccoli, Beets
Fruits: Blueberry, Pineapple
Nuts and seeds: Walnuts, Chia seeds
Oils: Coconut oil, Olive oil
Spices: Turmeric, Ginger
Heal your gut: Hippocrates said, “All disease begins in the gut.” Yes, that is right. There’s a good chance you have inflammation in your gut if you’re having problems with gas, bloating, or indigestion. Foods with gut-healing properties can be really beneficial:
Fiber-rich foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains.
Foods that are high in probiotics like fermented yogurt, sauerkraut.
Good fats like ghee and coconut oil.
Beneficial herbs like ginger, peppermint, triphala.
Exercise regularly: Exercise is the number one anti-inflammatory activity you can do. As low as 10-15 minutes of full-body stretching, yoga, pranayama, or just walking can be extremely beneficial in reducing inflammation. However, we must avoid over-exercising.
Stabilize blood sugar: You should fix your blood sugar if it fluctuates a lot. When your blood sugar levels are out of whack, it can lead to irregular hormone production and stress. Replace sugary fast food and refined carbohydrates with foods rich in fiber and healthy fats.
Reduce stress: Inflammation is worsened by chronic stress, worry, and anxiety. We may not be able to solve all of our problems in life, but we can definitely manage them. Meditation and prayer can really help. Self-improvement and following one’s passion are also beneficial.
Vitamin D: New research found that low vitamin D levels are linked to an increased risk of inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Vitamin D is a powerful immune regulator. Whether it is inflammation due to an injury or an autoimmune situation, vitamin D is something that can really help. So, get some sunlight for 20 minutes daily.
Sleep more: Lack of sleep will make you more vulnerable to stress and imbalance, which can lead to inflammation.
Go to bed early.
Allow it to happen naturally, don’t force yourself.
Don’t use an alarm, let nature wake you up.
It’s fine to sleep an extra hour.
Common Questions on Inflammation
What does anti-inflammatory mean?
Anti-inflammatory properties refer to a food, compound, activity, or drug’s ability to reduce inflammation and its effects such as pain, swelling, and heat in the body.
What are the 5 classic signs of inflammation?
There are five signs that acute inflammation is present:
Redness: The inflamed area appears red as blood flow increases.
Heat: The inflamed region feels worm because of the increased blood flow.
Swelling: Cytokines of immune response cause fluid accumulation
Pain: Pain is caused by ongoing inflammation and swelling.
Loss of functions: Loss of smell, loss of taste, the injured part is difficult to move.
What milk is best for inflammation?
We know that dairy causes inflammation. Instead of dairy, use coconut milk. Coconut milk is without a doubt, the best anti-inflammatory milk.
Is chronic inflammation permanent?
Chronic Inflammation may be reduced or even reversed with dietary and lifestyle changes. The human body is known for its ability to repair itself from damages. We just need to support it.